
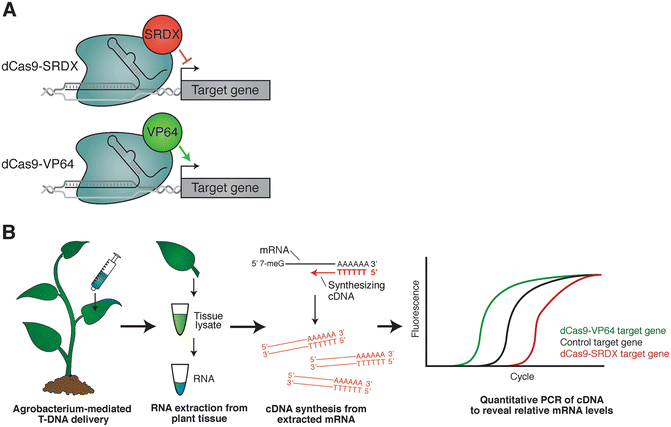
To conquer these known and latent restrictions, CRISPR/Cas system has been reprogrammed to regulate gene expression transcriptionally by catalytical manipulation of Cas9 endonuclease, dead mutation of Cas9 catalytic sites (dCas9), RuvC D10A and HNH H840A. Meanwhile, the inevitable lethality caused by loss of function of critical genes perturbed the application of CRISPR in some scenarios (Han et al., 2010, Kabir et al., 2017). However, since the introduction of DSB by CRISPR/Cas is irreversible and persistent, there is a concern about the chromosomal instability and rearrangements, even chromosome loss (Cullot et al., 2019, Kosicki et al., 2018, Rayner et al., 2019). The application of this strategy is of paramount importance for molecular engineering in many organisms. The DNA repair system of host, non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) or homology-directed repair (HDR), is elicited to repair the target gene, which may alter the sequences of this gene, such as indels of nucleotide(s) or fragment replacement (Barman et al., 2020). Cas9, identified from a type II CRISPR system, is an DNA endonuclease and can be guided by single-guide RNA (sgRNA) to the customized target site specifically by RNA-DNA base pairing, the double stranded break (DSB) of the targeting sequence ensued. During the past decades, substantial revolution for genome editing has been witnessed, from zinc finger nuclease (ZFN) and transcription activation-like effector nuclease (TALEN), to clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR)-associated (Cas) nuclease, which took the biological world by storm since its incipience (Bortesi and Fischer, 2015, Komor et al., 2017, Wang et al., 2016). To deciphering these mysterious processes, proper biotechnology techniques, especially tools for gene manipulation, is pivotal (Chinnusamy et al., 2007, Hernandez-Garcia and Finer, 2014, Mack and Nachman, 2017, Nakayama and Kataoka, 2019, Sun et al., 2018). The expression of genes, as building blocks for the normal function of cells, are regulated precisely in vivo to orchestrate the complicated activity of each creature. Our data broaden the application of CRISPR/dCas9 based transcriptional regulation and provide great opportunities to investigate the function of essential genes in common wheat. The study on the tRNA-processing system in CRISPR/dCas9 based transcriptional regulation system demonstrated that this robust multiplex targeted tool can be incorporated to the CRISPR/dCas9 system to facilitate the target regulation of several genes’ transcriptional level. Our results showed that dCas9 fused activation or repression domain could increase or decrease the transcriptional level of target gene effectively in stable transgenic lines of wheat. For target gene’s repressing expression transcriptionally, 3×SRDX repression domain was conjugated to the C-terminus of dCas9 in frame.
SRDX RECOGNITION DOMAIN ACTIVATOR
To improve target gene’s expression, we generated transcriptional activator by fusing 6×TAL-VP128 activation domain to the C-terminus of dCas9 in frame. Here, we exploited the CRISPR/dCas9 system to manipulate the transcriptional level of target genes in common wheat. The inactivation of catalytical site in Cas9 (dCas9) has been reprogrammed as an effective approach to regulate the transcriptional level of target genes, especially for the functionally essential genes and redundant genes. Extensive experiments are conducted on the DREAMER and DEAP datasets, and the results show the superiority of our proposed method.The application of CRISPR/Cas9 system for gene editing, as a technical coup for biotechnology, is worldwide and encompasses multiple of species. We compute the SPD matrix based on the covariance as a feature and make a novel attempt to combine prototype learning with the Riemannian metric. Our method jointly exploits feature adaptation with distribution confusion and sample adaptation with centroid alignment. To solve this problem, we propose a domain adaptation SPD matrix network (daSPDnet) that can successfully capture an intrinsic emotional representation shared between different subjects. Recently, developing an effective brain-computer interface with a short calibration time has become a challenge. The conventional method involves the collection of a large amount of calibration data to build subject-specific models. Due to individual variability, training a generic emotion recognition model across different subjects is difficult. Emotion plays a vital role in human daily life, and EEG signals are widely used in emotion recognition.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
